AgriTech and Urban Farming
AgriTech and urban farming represent innovative approaches to agriculture that leverage technology to enhance food production, sustainability, and accessibility in urban areas. AgriTech encompasses a broad range of technological advancements, including precision farming, IoT sensors, data analytics, and automated machinery, all aimed at optimizing agricultural practices. These technologies enable farmers to monitor and manage crops more efficiently, reduce resource usage, and increase yields. Urban farming, on the other hand, brings food production into cities through methods like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics. By growing food closer to where it is consumed, urban farming reduces transportation costs and carbon footprints while ensuring fresh produce is readily available in densely populated areas. Together, AgriTech and urban farming address the challenges of feeding a growing global population, mitigating the environmental impact of traditional farming, and enhancing food security. These approaches also support local economies and create opportunities for urban residents to engage in sustainable agricultural practices, transforming cities into hubs of innovative food production.

What is AgriTech, and how does it benefit modern agriculture ?
AgriTech, short for agricultural technology, refers to the application of advanced technologies to improve the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of agricultural practices. This encompasses a wide range of innovations, including precision farming, IoT sensors, drones, data analytics, and automated machinery. Precision farming, for instance, uses GPS technology and IoT sensors to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health in real-time, allowing farmers to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides more accurately and efficiently. Drones and satellite imagery provide detailed aerial views of fields, helping to identify areas that require attention. Data analytics enables the processing of vast amounts of information to make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and resource management. Automated machinery, such as self-driving tractors and robotic harvesters, reduces labor costs and increases operational efficiency. These technological advancements not only enhance crop yields and reduce waste but also minimize the environmental impact of farming by optimizing resource usage and reducing chemical inputs. AgriTech benefits modern agriculture by addressing the challenges of feeding a growing global population, ensuring food security, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
How does urban farming contribute to food security in cities ?
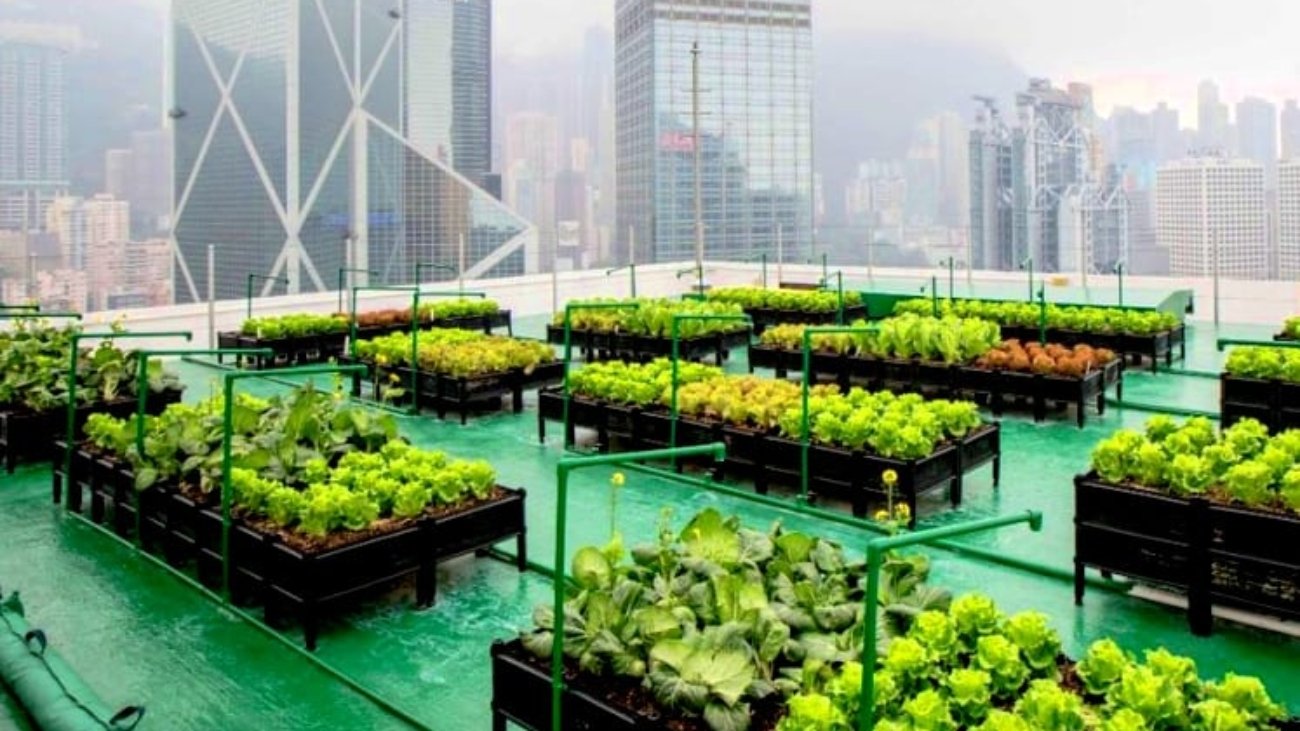
Urban farming plays a crucial role in enhancing food security in cities by bringing food production closer to urban populations. This practice involves growing food within city environments using innovative methods such as vertical farming, hydroponics, aquaponics, and rooftop gardens. Vertical farming utilizes stacked layers to grow crops in a controlled indoor environment, maximizing space efficiency and enabling year-round production. Hydroponics and aquaponics are soil-less farming techniques that use nutrient-rich water to grow plants, significantly reducing water usage compared to traditional farming. By producing food locally, urban farming reduces reliance on long supply chains, which can be vulnerable to disruptions such as natural disasters, transportation issues, or economic instability. This ensures a steady supply of fresh produce to urban residents, contributing to food security. Additionally, urban farming can make nutritious food more accessible and affordable, particularly in food deserts where access to fresh produce is limited. It also promotes community engagement, as local residents can participate in growing and harvesting food, fostering a sense of ownership and connection to their food sources. By integrating food production into urban settings, urban farming addresses food security challenges and supports resilient, sustainable urban communities.
What are the business opportunities available in the AgriTech sector ?
The AgriTech sector presents numerous business opportunities across various areas of agriculture. Startups and established companies can develop and market innovative technologies such as IoT sensors, drones, and data analytics platforms that help farmers monitor and manage their crops more effectively. Precision farming solutions that provide real-time data on soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health are in high demand, as they enable farmers to optimize resource usage and increase yields. Automated machinery, including robotic harvesters and self-driving tractors, offers significant opportunities to reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency on farms. Additionally, there is a growing market for sustainable farming solutions that minimize environmental impact, such as water-efficient irrigation systems and organic fertilizers. AgriTech companies can also explore opportunities in genetic engineering and biotechnology to develop pest-resistant or climate-resilient crop varieties. Moreover, the rise of urban farming creates demand for vertical farming systems, hydroponic and aquaponic setups, and smart greenhouse technologies. By addressing the evolving needs of modern agriculture and urban food production, businesses in the AgriTech sector can tap into a rapidly expanding market and contribute to sustainable food systems.
How does urban farming positively impact the environment ?
Urban farming positively impacts the environment in several ways. By bringing food production into urban areas, it reduces the need for long-distance transportation of produce, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions and the carbon footprint associated with food distribution. Urban farming methods, such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics, are highly efficient in terms of space and resource usage. Vertical farming, for instance, utilizes vertical space to grow crops in stacked layers, allowing for higher yields per square foot compared to traditional farming. Hydroponic and aquaponic systems use significantly less water than soil-based agriculture, as water is recirculated and reused, reducing overall water consumption. These methods also typically use fewer pesticides and fertilizers, minimizing chemical runoff and soil contamination. Urban farming can contribute to urban greening, as rooftop gardens, green walls, and community gardens enhance biodiversity and create green spaces within cities. These green spaces can help mitigate the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and provide habitat for pollinators and other wildlife. Additionally, by promoting local food production, urban farming encourages sustainable consumption patterns and raises awareness about the importance of environmentally friendly practices. Overall, urban farming supports more sustainable and resilient urban ecosystems.
What challenges do businesses encounter when operating in the AgriTech and urban farming sectors ?
Businesses in the AgriTech and urban farming sectors face several challenges that can impact their operations and growth. One significant challenge is the high initial investment required for developing and implementing advanced technologies. Precision farming equipment, IoT sensors, drones, automated machinery, and indoor farming systems can be costly to design, produce, and maintain. Securing funding and demonstrating return on investment (ROI) can be difficult, especially for startups. Additionally, there is the challenge of integrating these technologies with existing agricultural practices and ensuring that farmers and urban growers have the necessary skills and knowledge to use them effectively. Training and support services are essential but can be resource-intensive.
Regulatory hurdles and compliance with local, national, and international agricultural and environmental regulations can also pose challenges, requiring businesses to navigate complex legal landscapes. For urban farming, securing suitable spaces within city environments and dealing with zoning laws and building codes can be difficult. Market acceptance is another challenge, as consumers and traditional farmers may be resistant to adopting new technologies and practices. Businesses must invest in education and marketing efforts to build trust and demonstrate the benefits of their innovations.