“Unlocking the Future: How New Trends in Digital Twin Technology Can Boost Startup Success”
Digital twin technology is rapidly evolving, offering exciting new ways for startups to improve their operations and product development. With advancements like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT), startups can now use digital twins in more powerful and effective ways. This article looks at how these new trends can help startups make better decisions, manage resources more efficiently, and drive innovation.
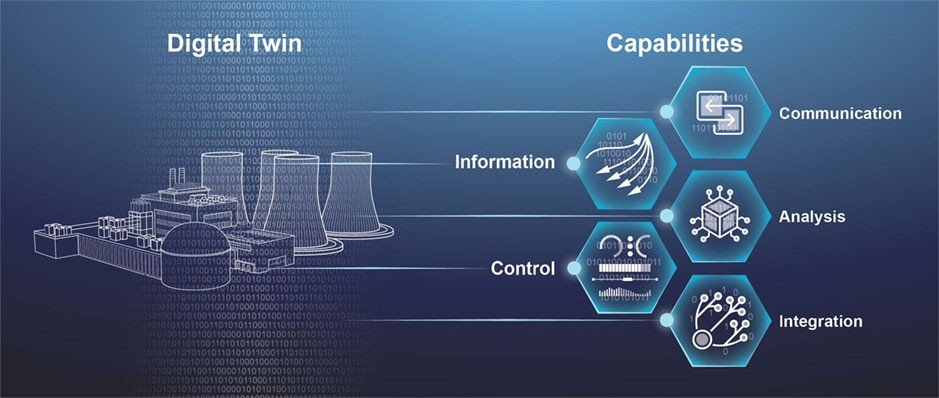
How can digital twins transform the way startups approach product design and development from inception to market launch?
Digital twins are transforming the approach to product design and development by providing a comprehensive, virtual representation of a product or process. This technology enables startups to visualize, test, and refine their ideas in a digital environment before committing to physical prototypes. From the inception stage, startups can use digital twins to model the product’s design, simulate its functionality, and anticipate potential issues. This early-stage testing allows for rapid iteration and optimization of design elements without the cost and time associated with creating physical prototypes.
As development progresses, digital twins help in simulating various real-world scenarios that the product may encounter. For example, a startup developing a new piece of machinery can use a digital twin to simulate different operating conditions, assess performance under stress, and predict failure points. This proactive approach helps identify and address design flaws before the product is manufactured, reducing the risk of costly modifications later.
Moreover, digital twins facilitate collaboration by providing a single, updated version of the product that all team members can interact with. This centralized model helps ensure that everyone—from engineers to marketing teams—is aligned with the product’s specifications and development status. The ability to test changes in real-time and see their impact on the product helps startups make informed decisions quickly.
By leveraging digital twins throughout the product lifecycle, startups can streamline the development process, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market. This technology not only enhances design accuracy but also improves the ability to respond to market feedback and adapt the product accordingly, giving startups a competitive edge and increasing the likelihood of successful market entry.
What are the key challenges that startups might face when integrating digital twin technology into their existing workflows, and how can they overcome them?
Integrating digital twin technology into existing workflows can present several challenges for startups. One primary challenge is the cost and complexity associated with implementing digital twins. Developing and maintaining a digital twin requires investment in specialized software, hardware, and expertise. For startups with limited budgets, this initial investment can be a significant hurdle. Additionally, integrating digital twins into established workflows necessitates changes in processes and systems, which can be met with resistance from team members who are accustomed to traditional methods.
Another challenge is ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the data used to create and update digital twins. Digital twins rely on high-quality data to accurately represent the physical product or process. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed simulations and incorrect insights. Startups must invest in robust data collection and management systems to ensure the reliability of their digital twins.
To overcome these challenges, startups should start with a phased approach to implementation. Begin by identifying specific use cases where digital twins can deliver the most value, and pilot the technology in those areas. This approach allows startups to demonstrate the benefits of digital twins and build internal support. Investing in training and support for team members will also help ease the transition and address resistance to change.
Startups should prioritize data quality by establishing clear data management practices and leveraging advanced data collection tools. Collaborating with technology providers and industry experts can also help navigate the complexities of integrating digital twins and ensure successful implementation.
In what ways can digital twins be used to simulate different market scenarios and customer interactions before a product is launched?
Digital twins offer powerful capabilities for simulating various market scenarios and customer interactions before a product is launched. By creating a virtual model of a product and its environment, startups can explore how different factors might affect its performance and reception in the market.
One way digital twins can be used is by modeling customer interactions and feedback. Startups can simulate how customers will use the product, assess their responses to different features, and evaluate how changes might impact user satisfaction. This allows startups to identify and address potential issues or improvements before the product is introduced to the market.
Digital twins also enable startups to test different market scenarios, such as varying levels of demand, competitive actions, or economic conditions. By running simulations based on these scenarios, startups can gain insights into how their product might perform under different circumstances and adjust their strategies accordingly. For example, a startup could simulate how a new product would fare in a high-demand environment versus a saturated market, helping them optimize their marketing and sales strategies.
Digital twins can be used to test pricing strategies, promotional campaigns, and distribution channels. By simulating these elements, startups can predict their impact on product success and make data-driven decisions to refine their go-to-market strategy.
Digital twins provide a risk-free environment to test and refine various aspects of a product and its market strategy, allowing startups to make informed decisions and increase the likelihood of a successful launch.
How do digital twins contribute to more efficient resource management and cost savings in startup operations?
Digital twins contribute to more efficient resource management and cost savings by providing real-time insights into the performance and utilization of resources. This technology allows startups to create virtual models of their operations, including production processes, supply chains, and equipment. By analyzing these models, startups can identify inefficiencies and optimize resource usage.
One key area where digital twins drive cost savings is in production optimization. For example, startups can use digital twins to simulate different production scenarios, such as varying production speeds, equipment configurations, or material inputs. This allows them to identify the most efficient processes and reduce waste. By optimizing production schedules and minimizing downtime, startups can lower operational costs and improve overall productivity.
Digital twins also help startups manage their supply chains more effectively. By modeling the entire supply chain, startups can track inventory levels, monitor supplier performance, and predict potential disruptions. This visibility enables better planning and decision-making, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking and improving cash flow.
Digital twins enable startups to implement predictive maintenance strategies. By continuously monitoring equipment performance and using digital twins to simulate potential failures, startups can schedule maintenance activities proactively rather than reactively. This approach reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of equipment, leading to significant cost savings.
digital twins provide startups with a comprehensive view of their operations, allowing for better resource management, cost savings, and improved efficiency.
Can you provide examples of startups that have successfully implemented digital twins and the specific benefits they experienced?
Several startups have successfully implemented digital twin technology and achieved significant benefits. For example, Augmented Reality (AR) startup PTC has used digital twins to enhance its product development and customer engagement processes. By creating virtual models of its AR solutions, PTC can simulate how customers interact with their products, allowing for improvements based on real-time feedback. This has led to more effective product designs and a better user experience.
Another example is Sensorcom, a startup specializing in IoT sensors and analytics. Sensorcom uses digital twins to optimize its sensor networks and monitor environmental conditions. By creating virtual replicas of their sensor systems, Sensorcom can analyze performance, detect anomalies, and predict maintenance needs. This approach has resulted in improved system reliability and reduced operational costs.
Grid.ai, a startup focused on energy management, has also successfully used digital twins. Grid.ai creates virtual models of energy grids to simulate and optimize their performance. By analyzing different scenarios, Grid.ai can predict energy demand, manage load distribution, and reduce energy costs. This has enabled the company to provide more efficient and cost-effective energy solutions to its clients.
These examples highlight how digital twins can provide startups with valuable insights, enhance product development, and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging digital twin technology, these startups have gained a competitive edge and achieved their business goals more effectively.
What role does data quality play in the effectiveness of digital twins for startups, and how can startups ensure they are working with accurate data?
Data quality is critical to the effectiveness of digital twins because the accuracy and reliability of the virtual model depend on the quality of the input data. Digital twins rely on data from various sources, such as sensors, simulations, and historical records. If this data is inaccurate or incomplete, the digital twin may produce unreliable results, leading to incorrect insights and poor decision-making.
To ensure data quality, startups should implement rigorous data management practices. This includes establishing clear protocols for data collection, validation, and storage. Startups should use high-quality sensors and data acquisition tools to gather accurate and reliable data. Regularly calibrating and maintaining these tools will help prevent data drift and ensure ongoing accuracy.
Startups should invest in data cleaning and validation processes to identify and correct any discrepancies or errors in the data. This involves checking for inconsistencies, removing duplicates, and verifying data against trusted sources. Implementing automated data quality checks and monitoring systems can also help maintain data integrity.
Collaboration between teams is essential for ensuring data quality. Data from different departments, such as engineering, design, and operations, should be integrated and aligned to provide a comprehensive view of the product or process. Regular communication and data sharing among teams will help identify and address any issues related to data accuracy.
Overall, maintaining high data quality is crucial for the effectiveness of digital twins. By implementing robust data management practices and ensuring accurate data collection, startups can enhance the reliability of their digital twins and make more informed decisions.
How can startups leverage digital twins to enhance their decision-making processes and reduce risks associated with product development?
Startups can leverage digital twins to enhance decision-making and reduce risks by using virtual models to simulate and analyze different scenarios. Digital twins provide a comprehensive view of a product or process, allowing startups to test various factors and predict their impact on outcomes.
One way startups can use digital twins for decision-making is by running simulations to evaluate different design options or operational strategies. For example, a startup developing a new product can use a digital twin to test how changes in design or functionality might affect performance, cost, and user experience. This allows startups to make data-driven decisions and choose the best options based on simulated results.
Digital twins also help reduce risks by identifying potential issues early in the development process. By simulating various scenarios, startups can predict and address potential problems before they occur in the real world. For example, digital twins can be used to test how a product will perform under different environmental conditions or user behaviors. This proactive approach helps startups avoid costly mistakes and improve product reliability.
Digital twins enable startups to monitor real-time data and make adjustments based on current conditions. By integrating digital twins with IoT sensors and data analytics, startups can track the performance of their products and processes in real-time. This allows for timely adjustments and interventions, reducing the risk of failures or inefficiencies.
digital twins provide startups with valuable insights and tools to make informed decisions, reduce risks, and enhance product development. By leveraging this technology, startups can improve their decision-making processes and increase the likelihood of successful product launches.
What are the potential limitations or pitfalls of using digital twins for startups, and how can they be addressed to maximize the technology’s benefits?
While digital twins offer many advantages, there are potential limitations and pitfalls that startups should be aware of. One limitation is the complexity and cost of developing and maintaining digital twins. Creating an accurate digital twin requires specialized software, hardware, and expertise, which can be expensive and challenging for startups with limited resources.
Another potential pitfall is the reliance on data quality and accuracy. Digital twins depend on high-quality data to produce reliable simulations and insights. If the data used to create and update the digital twin is inaccurate or incomplete, it can lead to flawed results and decision-making.
Integrating digital twins into existing workflows can be challenging. Startups may face difficulties in aligning digital twin technology with their current processes and systems. Resistance to change from team members accustomed to traditional methods can also hinder the adoption of digital twins.
To address these limitations and maximize the benefits of digital twins, startups should start with a clear implementation plan and focus on specific use cases where digital twins can deliver the most value. Investing in training and support for team members will help ease the transition and address resistance to change.
Startups should also prioritize data quality by implementing robust data management practices and using accurate data collection tools. Collaborating with technology providers and industry experts can help navigate the complexities of digital twin technology and ensure successful implementation.
By addressing these challenges and focusing on strategic implementation, startups can effectively leverage digital twins to enhance their product development and operational efficiency.
How can digital twins facilitate collaboration and communication among different teams within a startup, such as design, engineering, and marketing?
Digital twins facilitate collaboration and communication among different teams within a startup by providing a shared, interactive model that all teams can access and use. This centralized virtual model serves as a single source of truth, ensuring that everyone involved is aligned with the product’s specifications and development status.
For example, design teams can use digital twins to visualize and test their designs in a virtual environment, while engineering teams can assess how these designs will impact the product’s performance and functionality. Marketing teams can also access the digital twin to understand the product’s features and benefits, allowing them to develop more accurate and targeted marketing strategies.
Digital twins promote better alignment and coordination by providing a real-time view of the product’s development and performance. Teams can collaborate more effectively by sharing insights, feedback, and updates through the digital twin model. This reduces misunderstandings and ensures that all teams are working towards the same goals.
Digital twins enable real-time updates and feedback, allowing teams to make adjustments based on current information. For example, if the engineering team identifies a design flaw, they can update the digital twin, and the design team can immediately see and address the issue. This iterative process helps streamline decision-making and improves overall product development.
Digital twins enhance collaboration and communication by providing a unified, interactive model that facilitates coordination among different teams. By using digital twins, startups can improve teamwork, reduce miscommunications, and accelerate the product development process.
What future trends or advancements in digital twin technology could further benefit startups, and how can they prepare for these changes?
Future trends and advancements in digital twin technology are likely to bring even greater benefits to startups. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with digital twins. These technologies will enhance the predictive capabilities of digital twins, allowing for more accurate simulations and automated insights. For example, AI algorithms can analyze data from digital twins to identify patterns, predict potential issues, and recommend improvements, providing startups with valuable, data-driven insights.
Another trend is the increased integration of digital twins with the Internet of Things (IoT). By connecting digital twins to IoT devices, startups can gather real-time data from physical products and processes, enabling more accurate and up-to-date virtual models. This integration will enhance the ability to monitor and optimize operations in real-time, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
Advancements in data visualization and virtual reality (VR) are also expected to enhance the use of digital twins. Improved visualization tools will allow startups to interact with their digital twins in more immersive and intuitive ways, making it easier to analyze complex data and make informed decisions. VR technology will enable more realistic simulations and interactive experiences, enhancing the ability to test and refine products.
To prepare for these changes, startups should stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in digital twin development. Investing in ongoing training and technology upgrades will help ensure that teams are equipped to leverage new advancements effectively. Additionally, fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability will position startups to take advantage of future developments in digital twin technology.
By staying ahead of trends and preparing for technological advancements, startups can maximize the benefits of digital twins and continue to drive innovation and success in their operations.
The future of digital twin technology is full of promise for startups. New developments in AI, IoT, and data visualization will make digital twins even more useful for improving products and operations. By keeping up with these trends and integrating them into their strategies, startups can gain valuable insights, innovate faster, and succeed in a competitive market. Embracing these changes will help startups stay ahead and achieve long-term success.